It’s especially tricky to choose between Live Agent Training (LATs), simulants, and simulators, as they each come with certain pros and cons. While each training situation demands different solutions, there are some key factors to keep in mind when researching. These include:
- Realism
- Environmental impact
- Scenario replication
- Indoor use
- Outdoor use
- Regulatory impact
Keep reading for a breakdown of each of these considerations, including a more comprehensive comparison chart between Live Agent Training (LATs), simulants, and simulators.
Realism
This tends to be an overlooked aspect of training, with the ease of index card use regularly eclipsing the import of true-to-life experience. Keep in mind, however, that realism has been shown to be key to developing muscle memory and retaining key information.
As live agent training makes use of controlled quantities of real sources, it tends to be valued for its realism, especially in a CBRN environment. LATs are the closest students can get to a real experience, which is why they have become a popular option.
The problem with LATs, however, is that they fall under regulatory, economic, environmental, and time constraints. Simulants are another option here, as they make use of relatively safer chemicals, however it can be challenging to identify chemicals which accurately replicate live sources. In many situations, the realism can be lost due to chemicals which don’t appropriately mimic live agents.
Simulators, on the other hand, allow for Real Experience Training at any time, and in any place, without needing to worry about regulatory constraints and environmental impact. With the right technology, trainers and trainees won’t be impacted by the lack of live agents during the scenario.
Regulatory Impact
Due to the hazardous nature of the materials used, LATs are subject to intense regulatory scrutiny. Although simulant training uses chemical substances which are relatively safer than live agents, many are not biodegradable and can build up over time if used continuously in one area. Some have also been known to cause expensive damage to the operational detectors used to sense the simulants, especially if contaminated internally. Any resulting regulations could restrict simulant training, albeit to a lesser degree than LATs.
This is where Real Experience Training simulators have a significant benefit over their live agent and simulant counterparts. As these simulators do not pose any risk to health, safety, or the environment, they aren’t subject to the same regulations. Instructors are free to use these simulators when and where they want, without needing to navigate through the red tape that comes up with hazardous material use.
Environmental Impact
Both LATs and simulants pose a risk to the environment, especially during training, as common mistakes can lead to unintended releases and other hazardous situations. Operators need to follow strict regulations when handling these materials, which in many cases limits certain types of training scenarios.
Real Experience Training simulators, however, do not pose any environmental hazards. Teams can safely train anywhere and under any condition, which makes simulators the preferable option when considering environmental impact.
Scenario replication
Replicating key scenarios, especially with little or no variance between events, is a necessary but challenging task. Simulants are unfortunately difficult to replicate, as they involve a variety of chemicals which may not behave similarly to the live agents targeted in the exercises. They can also contaminate and saturate the training area with a detrimental impact on subsequent exercises.
LATs are invaluable for ensuring a replicable event, especially when the goal is for trainees to get a more in-depth understanding of key chemical hazards and their effects. However, they’re subject to strict regulations, location and time restraints, and require trainees to already have a high level of proficiency with the materials.
Real Experience Training simulators also offer repeatability with minimal variance. The difference is that they don’t utilise the hazardous materials which are subject to health and safety concerns. This allows trainees without high levels of proficiency in hazardous materials to practise and repeat key scenarios.
→Download Now: How To Source Simulator Detectors for CBRNe & HazMat Training
Indoor use
In order to provide the closest resemblance to real agent reactions, many instructors utilise wet simulants. However, most of these can only be used outdoors.
LATs are better options when training inside buildings and other covered locations. However, Real Experience Training simulators offer more flexibility, as many LATs require specifically designed, unused and/or remote buildings which pose reduced health and safety hazards.
Outdoor use
This is where LATs are potentially challenging to utilise. When planning LAT training outdoors, all elements of the scenario have to be rigorously controlled. Weather conditions, the nature and quantity of the chemical or biological agent, and even the time of day must all be taken into account. This can potentially limit training situations.
Simulants are an alternative option to LATs, but instructors still need to take the weather, health, safety, and the environment into account.
Real Experience Training simulators are built for either indoor or outdoor use, and can function in any meteorological condition.
A Wider Comparison
The chart below provides a more comprehensive overview of key differences between LAT, simulant, and simulator training:
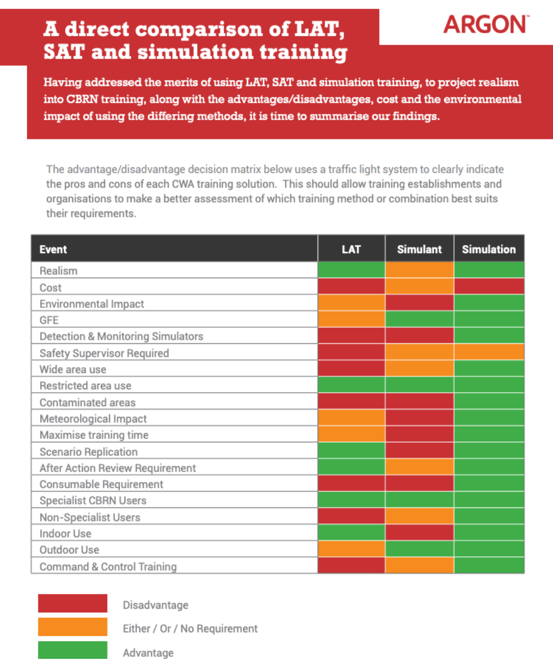
As illustrated, there are various factors to consider when determining which type of training equipment and materials to use for a given scenario. Researching which delivers the most realism, repeatability, and replication is key, but it’s also important to note where the scenario should take place and how this may affect health, safety, and the environment.
Utilising Real Experience Training simulators might be the best option when taking these variables into account, but it may be difficult to move away from tried-and-tested LAT and simulant training.
To learn more about Argon’s simulators, including the increasingly important role they play in boosting the authenticity of training exercises, download our free ebook: How To Source Simulator Detectors for CBRNe and HazMat Training. This guide also offers advice for sourcing and procuring the essential equipment that you need to implement effective CBRN training scenarios.




